|
Author:Thomas
A. Lang and Douglas G. Altman
Title:Statistical
analyses and methods in the published literature:The
SAMPL guidelines.
此篇為SAMPL指引的最新版,也算是第三版。此篇之簡介(introduction)說明在1966年,第一次有期刊針對生醫論文的統計品質提出評論(1)。在近年來,有數十篇與期刊論文統計問題之評論文章(2-18),此篇為SAMPL
Guide之最新版,包括一些進階統計技術使用評論(19-25)。
第三版之內容如下:
Ⅰ、統計方法的報導
一、初期分析(preliminary
analyses)
1.
在進行分析之前,對於原始數據之處理都需要報導確認,例如對於數據進行數學公式轉換,以接近常態分佈,或是以比例值顯示數據,將連續性數據以分類數據表示,將分類數據加以結合。
二、主要分析(Primany
analyses)
1.
描述進行分析之目的。
2.
確認使用分析的每一變數(Variable),並且以敘述統計加以描述。
3.
對於診斷研究相當重要的變數,儘可能顯示其最小的差異性。
4.
對於研究目的所使用的分析方法加以完整性的報導。
5.
對於每項分析所使用的方法分別描述,避免以概括方式列出使用的統計方法。
6.
對於分析的方法,要驗證其假設之正確性,尤其是a.以非參數檢定法分析Skew數據,b.以成對檢定技術分析成對數據,c.執行線性迴歸,而其關係是否線性相關。
7.
以相同的數據群進行多重比較,要顯示其信賴水準是否調整與如何調整。
8.
有多少離群數據(outlying
data),在分析過程中如何處理。
9.
使用單尾或雙尾檢定,如何判別使用單尾?
10.
對於統計顯示水準加以報導(例如α
= 0.05)。
11.
說明使用的統計軟體與其版本。
三、補充說明(Supplementary
analyses)
1.
對於任何輔助(ancillary)分析的使用方法,例如敏感性分析(sensitivity),遺失數據之補遺(imputation
of missing values),對假設條件之檢定等。
2.
對於事後分析(post-hoc)要加以確認,包括非計劃之次族群分析等。
Ⅱ、統計結果之報導
一、敘述統計之報導
1.
數據,尤其是量測數據,要儘量精確(precision)。為了容易理解與簡單化,可以四捨五入。
2.
對於每個分析要報導所有樣本數目與分組數目。
3.
對所有百分比要報導分子與分母。
4.
對常態分配之數據,報導平均值與標準差(SD),其形式為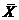 ±SD。 ±SD。
5.
非常態分佈之數據,要列出中數,四分之一位數,四分之三位數,說明內四分位距之上限與下限。
6.
不要使用標準偏差(Standard
error of the mean, SE)用以表示數據之變異性。
7.
以表、圖顯示據。表格代表確實數值,圖形表示所有數據之評估。
二、風險,比例之比值(risk,
rates, ratios)
1.
確定數值
a.
比例:發生率
(incidence rates); 存活率 (survival rates).
b.
比值:勝算比(odds
ratio), 相對風險比(hazards
ratios).
c.
風險:絕對風險(absolute
risks),相對風險差異(relative risk differences)。
2.
確認報導數值之分子與分母
3.
每個試驗,比例值之時間週期要確認。
4.
比例之族群要加以報導(例如 x
100, x 10,000)。
5.
對於風險,比例與比值要求報導其信賴區間。
三、統計檢定
1.
描述統計檢定之狀態。
2.
對於分析之變數(Variables)加以確認,對每一變數之數以適當的敘述統計加以描述。
3.
對於醫療(clinically)性的重要差異值加以確認。
4.
對於相等性(equivaleve)與非推論性(non-inferiories)之研究,報導族群間最大的不同。在生物相等性或許可以接受,但是在統計之差異也需要報導。
5.
對於檢定加以說明:單尾,雙尾,或成對試驗。
6.
對於數據之假設條件(例如常態分佈)需要加以檢定。
7.
對於統計顯著性(例如 α =
0.05)加以報導。
8.
對於主要之分析結果,例如族群中之差異,診斷敏感性(diagnostic
sensitivity),迴歸之斜率等,需要報導其精確性,例如其95%信賴區間。
9.
不能使用SE值表示估計值之精密性,單一之SE值只代表68%信賴區間。
10.
統計檢定之結果,列出P值時,儘可能有小數點兩位,例如P
= 0.03 或 P = 0.22,不要只寫出P
< 0.05。也不要只使用”NS”。 太小的P值其表示方法為
“P < 0.001”。
11.
多重比較是否進行調整,需要報導。
四、相聯分析(Association
analyses)
1.
描述為何使用相聯分析。
2.
以敘述統計確變數與結果(Summary)。
3.
確認使用之檢定方法,單尾或雙尾。
4.
相聯檢定(例如卡方分析)需要報導P值。
5.
對於參值,例如(Phi)係數,要報導其信賴區間。不能只用Low,Moderate與high描述其關連。要考慮其生物上的關聯性。
6.
對於Primary
compassions,以列聯表進行分析。
五、相關分析
1.
描述使用相關分析之目的。
2.
綜合報導每一變數的敘述統計結果。
3.
確認使用之相關分析係數,Pearson
或Spearman。
4.
確認分析之假設條件。
5.
說明信賴水準,以顯示相關係數是否有統計顯著性。
6.
進行相關係數報導,除非對其範圍已有定義,否則不要以Low
,Moderate, high加以表示。對於生物上的意義加以考慮。
7.
不論是否顯著,報導相關係數(95%)信賴區間。
8.
可以以數據分佈圖表示相關性,樣本大小,相關係數,信賴區間與P值在圖上需要說明。
六、迴歸分析
1.
描述迴歸分析之目的。
2.
確認分析中的變數,以敘述統計加以描述。
3.
確認假設條件,例如線性要檢定其線性。
4.
對於離群值要加以報導。
5.
對於遺失數據之處理需要報導。
6.
對於多重迴歸,要報導a.使用之信賴區間,b.變數之評估結果,c.重合性,d.變數之選擇方法(例如t檢定)。
7.
每一迴歸變數之信賴區間與P值,最好以表格表示。
8.
對於線性迴歸,可以以圖形顯示,並且列出迴歸直線,但是直線不能超過數據群之最大與最小值。
9.對模式的適合性要列出其評估數值(measure),例如線性迴歸的r2或是多重迴歸的R2。
10.列出為何與驗證模式。
七、變方分析與共變異數分析
1.描述進行此分析的目的。
2.確認分析中所使用的變數(variables)與敘述統計以討論每一變數。
3.對於分析的假設條件都要加以確認。例如以殘差
(residuals)確認是否為線
4.
確認假設條件,例如是否常態分佈。
5.
離群值與遺失數據之處理。
6.
確認變數是否有交互效應,如何檢定其交互效應。
7.
以表格表示結果,每一變數之P值,統計量,自由度等。
8.
如果有相關性,報導如何處理這些數據。
9.
對於模式的適應性要如何評估?
10.
列出為何與如何驗證模式。
八、存活分析
1.
解釋使用存活分析之目的。
2.
描述事件之起止時間。
3.
數據進行調查其環境背景。
4.
描述用以估計存活率之統計方法。
5.
確認假設條件。
6.
對每一族群,報導存活機率,包括信賴區間,參預之數目。
7.
報導存活時間之中數,包括信賴區間。
8.
以Kaplan- Meier
plot或表格顯示結果。
9.
說明二或多組存活曲線進行多重比較之統計方法,報導其統計檢定與P值。
10.使用迴歸模式報導,以說明變數與存活率之相關性。
11.
報導每一試驗之風險評估或相對風險比(hazard
ratio)之信賴區間。
九、Bayesian分析之報導
1.列出預先設定之或然率。
2.解釋如何預先選定。
3.描述所有的統計模式。
4.描述所有的分析技術
5.對後來選定之分配(posterior
distribution)描述其趨中特性與信賴度間隔。
6.評估與分析不同優先選擇之敏感性。
References
1. Lang T, Altman D.
Basic statistical reporting for articles published in clinical medical
journals: the SAMPL Guidelines. In: Smart P, Maisonneuve H, Polderman A
(eds). Science Editors’ Hand - book. European
2. Schor S, Karten I.
Statistical evaluation of medical journal manuscripts. J Am Med Assn.
1966;195:1123-8.
3. Prescott RJ, Civil
I. Lies, damn lies and statistics: errors and omission in papers
submitted to Injury 2010-2012. Injury. 2013;44:6-11.
4. Fernandes-Taylor
S, Hyun JK, Reeder RN, Harris AH. Common statistical and research design
problems in manuscripts submitted to high-impact medical journals. BMC
Res Notes. 2011;4:304.
5. Bosker T, Mudge JF,
Munkittrick KR. Statistical reporting deficiencies in environmental
toxicology. Environ Tox Chem. 2013;32(8):1737-9.
6. Vesterinen HM,
Egan K, Deister A, Schlattmann P, Macleod MR, Dirnagl U. Systematic
survey of the design, statistical analysis, and reporting of studies
published in the 2008 volume of the Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and
Metabolism. J Cerebr Blood Flow Metab. 2011;31:1064-72.
7. Kim JS, Kim DK,
Hong SJ. Assessment of errors and misused statistics in dental research.
Int Dent J. 2011;61:163-7.
8. Lee HJ, Jung SK.
The use of statistical methodology in articles in medical journals and
suggestions for the quality improvement of the Pediatric Allergy and
Respiratory Disease. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011;21:144-55.
9. Yim KH, Nahm FS.
Han KA, Park SY. Analysis of statistical methods and errors in the
articles published in the Korean Journal of Pain. Kor J Pain.
2010;23:35-41.
10. Al-Benna S, Al-Ajam
Y, Way B, Steinstraesser L. Descriptive and inferential statistical
methods used in burns research. Burns. 2010;36(3):343-6.
11. Robinson PM,
Menakuru S, Reed MW, Balasubramanian SP. Description and
reporting of surgical
data – scope for improvement? Surgeon. 2009;7(1);6-9.
12. Afshar K, Jafari
S, Seth A, Lee JK, MacNeily AE. Publications by the American Academy of
Pediatrics Section on Urology: the quality of research design and
statistical methodology. J Urol. 2009;182(4 Suppl):1906-10.
13. Barbosa FT, de
Souza DA. Frequency of the adequate use of statistical tests of
hypothesis in
original articles published in the Revista Brasileira de Anestesiologia
between January 2008 and December 2009. Rev Brasil Anestesiol.
2010;60:528-36.
14. Neville JA, Lang
W, Fleischer AB. Errors in the Archives of Dermatology and the Journal
of the American Academy of Dermatology from January through December
2003. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:737-40.
15. Kurichi JE,
Sonnad SS. Statistical methods in the surgical literature. J A Coll
Surg. 2006;202:476-84.
16. Scales CD, Norris
RD, Preminger GM, Vieweg J, Peterson BL, Dahm P. Evaluating the
evidence: statistical methods in randomized controlled trials in the
urological literature. J Urol. 208;180 1463-7.
17. Gaskin CJ,
Happell B. Power, effects, confidence, and significance: an
investigation of statistical practices in nursing research. Int J Nurs
Stud.
2014;51(5):795-806.
18. Jaykaran YP.
Quality of reporting statistics in two Indian pharmacology
journals. J Pharmacol
Pharmacother. 2011;2(2):85-9.
19. Mikolajczyk RT,
DiSilvestro A, Zhang J. Evaluation of logistic regression
reporting in current
obstetrics and gynecology literature. Obst Gynecol.
2008;111(2 Pt
1):413-9.
20. Burton A, Altman
DG. Missing covariate data within cancer prognostic studies: a review of
current reporting and proposed guidelines. Br J Cancer.
2004;91:4-8.
21. Mackinnon, A. The
use and reporting of multiple imputation in medical
research – a review.
J Intern Med. 2010;268:586-93.
22. Abraira V, Muriel
A, Emparanza JI, Pijoan JI, Royuela A, Plana MN. Cano
A, Urreta I, Zamora
J. Reporting quality of survival analyses in medical journals still
needs improvement. A minimal requirements proposal. J Clin Epidemiol.
2013;66:1340-6.
23. Kim M.
Statistical methods in Arthritis & Rheumatism – current trends. Arthr
Rheum. 2006;54:3741-9.
24. Reed JF, Salen P,
Bagher P. Methodological and statistical techniques: what do residents
really need to know about statistics? J Med Syst. 2003;27(3):233-8.
25. Aljoudi AS. Study
designs and statistical methods in the Journal of Family and Community
Medicine: 1994-2010. J Fam Commun Med. 2013;20(1):8-11
26. Lee CM, Soin HK,
Einarson TR. Statistics in the pharmacy literature. Ann Pharmacother.
2004;38(9): 1412–8.
|